| What is HiView genome browser? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
HiView is the first GWAS-variant centred Hi-C visualization tool, with the following three unique features:
HiView can leverage Hi-C information for better interpretation of GWAS variants.
HiView can facilitate the identification of potential target genes of GWAS variants.
HiView has incorporated multiple state-of-the-art Hi-C peak calling methods, enabling robust interpretation of Hi-C data.
|
|
|
| What data does HiView display? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
HiView displays Hi-C data, SNP data and gene data. HiView incorporates the fragment resolution (4 KB ~ 10 KB) Hi-C data published in Jin et al, Nature, 2013.
It is from human IMR90 cell line, with two experimental conditions: before TNF-alpha treatment and after TNF-alpha treatment.
There are six biological replicates for each experimental condition. For each biological replicate, HiView displays the following seven tracks:
- Observed count - The observed chromatin contact frequency between any two fragments.
- AFC expected count - The expected chromatin contact frequency between any two fragments.
Null distribution of chromatin contact frequency is calculate using the AFC method in Jin et al, Nature, 2014.
- Fit-Hi-C expected count - The expected chromatin contact frequency between any two fragments.
Null distribution of chromatin contact frequency is calculate using the Fit-Hi-C method in Ay et al, Genome Research, 2015.
- HMRF posterior probability - The posterior probability of biologically meaningful chromatin interaction obtained from HMRF peak caller.
- AFC p-value - The p-value of AFC peak caller.
- Fit-Hi-C p-value - The p-value of Fit-Hi-C peak caller.
- Fit-Hi-C q-value - The q-value of Fit-Hi-C peak caller.
Gene data
- Ensembl geneg - Ensembl gene prediction - archive Ensembl 54 (e.g. Eg:ENST00000359576).
- UCSC genes - UCSC gene (e.g. uc003jam.1).
- RefSeq genes - RefSeq gene (e.g. MET or NR_045839).
SNP data
- GWAS Catalog SNP - NHGRI catalogue of published genome-wide association studies (e.g. rs1600249).
- dbSNP build 130 - Single nucleotide polymorphisms dbSNP build 130 (e.g. rs1600249).
- dbSNP build 141 - Signle nucleotide polymorphisms dbSNP build 141 (e.g. rs371325881).
HiView is the first GWAS-variant centred Hi-C data visualization tool. Currently, it includes the following four types of tracks:
- DNA methylation
- Histone modification
- Transcription factor binding sites (TFBS)
- Known enhancers and promoters
HiView allows you to upload your own user-defined Hi-C data tracks. Users are allowed to upload or delete data files to HiView.
Users then associate data files with user-defined tracks. That is, specify which csv file is used/named as user-defined tracks.
For more details, please see the online tutorial on "Can I upload and use my own Hi-C data in generating the HiView figure?".
|
|
|
| How to visualize chromatin interactions using the default setting? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Please select the marker type, type the marker name, and then click the "Go" button.
HiView will display all Hi-C data within the topological domain containing that marker.
Annotations of a genetic marker:
- Chr:Bp - Users can specify the location of a genetic marker by typing in chromosome # and Bp # (e.g. chr8:11397047).
- SNPs (dbSNP build 130) - Users can specify a SNP name in the dbSNP build 130 (e.g. rs1600249).
- SNPs (dbSNP build 141) - Users can specify a SNP name in the dbSNP build 141 (e.g. rs371325881).
- GWAS catalogue SNPs - Users can specify a SNP name in the GWAS catalogue (e.g. rs1600249).
- RefSeq gene common name - Users can specify a common name in the RefSeq gene database(e.g. MYC).
- RefSeq gene NR_name - Users can specify a NR_gene name in the RefSeq gene database (e.g. NR_045839).
- Ensembl gene ENST_name - Users can specify a ENST_gene name in the Ensembl gene database (e.g. ENST00000359576).
- UCSC gene uc_Name - Users can specify a gene name in the UCSC gene database (e.g. uc003jam.1).
|
|
|
| How to navigate and fine tune the viewing window? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Users can navigate and fine tune the HiView figure using the navigation toolbars:
- Move left - Users can move the HiView figure left 10%, 20% and 50% by clicking the "<", "<<" and "<<<" buttons.
- Move right - Users can move the HiView figure right 10%, 20% and 50% by clicking the ">", ">>" and ">>>" buttons.
- Zoom in - Users can zoom in the HiView figure 1.5 time, 3 times and 10 times by clicking the "1.5X", "3X" and "10X" buttons right to the text of "zoom in".
- Zoom out - Users can zoom out the HiView figure 1.5 time, 3 times and 10 times by clicking the "1.5X", "3X" and "10X" buttons right to the text of "zoom out".
- Specify the viewing window - Users can specify the HiView figure by typing in chrN:StartBp-EndBp (e.g. chr8:11281384-12316727), and then click the "View" button.
- Reset the default viewing window - Users can reset the default viewing window at any time by clicking the "Go" button.
The HiView figure may show up slowly if the viewing window is larger than 100 MB. We recommend users not to zoom out >100X from the default viewing window.
|
|
|
| Which mode shall I specify for a track? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Users can specify different modes for a specific track
- Hide mode - The track will not be displayed.
- Dense mode - The track will be displayed in one row for different items. The annotation will not be displayed.
- Squish mode - The track will be displayed in multiple rows for different items. The annotation will not be displayed.
- Pack mode - The track will be displayed in multiple rows for different items but with a much larger space than "Squish" mode.
The annotation will be displayed. When more than 250 items are included in the HiView figure, the squish mode will be used instead of the pack mode.
- Full mode - Each item will be displayed in a single row. The annotation will be displayed.
The displayed items cannot exceed a pre-specified number (MAX_DISPLAY_ITEMS), default as 100.
This number can be changed in the configuration page.
For example, if HiView figure includes 130 genes, and MAX_DISPLAY_ITEMS=100,
the full mode will display the first 100 genes. If we set MAX_DISPLAY_ITEMS=150, all the 130 genes will be displayed.
|
|
|
| How to customize the HiView figure? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Users can customize the display of HiView figure by clicking the "Configure" button.
A configuration website will be displayed to customize the settings. There are three buttons in the bottom of the configuration website.
- View - Save the current setting in the HiView figure and return to the HiView main page.
- Save - Save the current setting in the HiView figure and display the configuration website for more customization.
- Reset - Reset to the default.
Users can configure the general setting in the configuration website.
- Image width - Image width in pixels .
Larger number will make the figure with a higher resolution when scaling back to the normal width in inches .
- Label area width - How large the left part of the figure is leaving blank (in characters).
- Text size - The font size (1 to 7).
- Track Height - The height of each track in dense and squish mode.
- Display the left text of tracks - Whether to display lest texts.
- Display the ruler - Whether to display the ruler.
- Display domain - Whether to display the domain.
- Display domain number - Whether to display the domain number.
- Display isoform - Whether to display the isoforms separately .
The order of all 27 tracks. Users can specify the order of the track by track number separated by comma.
- 27 tracks
1. Observed Count Combined
2. AFC Expected Count Combined
3. Fit-Hi-C Expected Count Combined
4. HMRF Posterior Probability Combined
5. AFC P Value Combined
6. Fit-Hi-C P Value Combined
7. Fit-Hi-C Q Value Combined
8. Observed Count Before TNF-alpha Treatment
9. AFC ExpectedCount Before TNF-alpha Treatment
10. Fit-Hi-C ExpectedCount Before TNF-alpha Treatment
11. HMRF Posterior Probability Before TNF-alpha Treatment
12. AFC P Value Before TNF-alpha Treatment
13. Fit-Hi-C P Value Before TNF-alpha Treatment
14. Fit-Hi-C Q Value Before TNF-alpha Treatment
15. Observed Count After TNF-alpha Treatment
16. AFC ExpectedCount After TNF-alpha Treatment
17. Fit-Hi-C ExpectedCount After TNF-alpha Treatment
18. HMRF Posterior Probability After TNF-alpha Treatment
19. AFC P Value After TNF-alpha Treatment
20. Fit-Hi-C P Value After TNF-alpha Treatment
21. Fit-Hi-C Q Value After TNF-alpha Treatment
22. gwasCatalog
23. snp130
24. snp141
25. EnsembleGenes
26. KnownGenes
27. RefGenes
28. User-defined Hi-C track 1
29. User-defined Hi-C track 2
30. User-defined Hi-C track 3
- Default track order
- "1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30"
- Arbitrary track order
e.g. "1,4,3,2,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30" or simply input "1,4,3".
- Reduced track order
In practice, users may not have all 27 tracks displayed. Users may display a few of them.
In this situation, users only need to specify the tracks they want to display.
- Poor-formatted track order
The track order must be some ordered unique numbers from 1 to 30,
separated by comma (","). If a string can not be recognized in this format, the default track order (1,2,...,30) will be used.
- Current track order
Current track order can be viewed in the configuration website.
If users input a new order (e.g. 1,4,3), it will replace the current order. Otherwise, the default track order will be used.
Users can specify the setting of each track.
- Display mode - Users can select from hide, dense, squish, pack and full modes.
- Color - Users can select from black, blue, grey, green and red.
- Left text - Users can specify the left text of each track, or leave it as blank.
- Top text - Users can specify the top text of each track, or leave it as blank.
These settings will be saved in your browser and the next time users open the browser,
the setting they used last time will be re-used. Users can choose to reset to default at any time.
|
|
|
| How to save the HiView figure? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Please move the mouse to the HiView figure, right click the mouse and select "Save as" in the pop-up menu.
Higher resolution figure can be created by specifying larger font size, larger image width in pixels, and larger track height.
|
|
|
| Can I extract Hi-C data after generating the HiView figure? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Yes, users can choose "Table" instead of "Figure" on the left top of the website to extract Hi-C data.
|
|
|
| Can I upload and use my own Hi-C data in generating the HiView figure? |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
Yes, users can upload and use his own Hi-C data in generating the HiView figure. In the configuration webpage, click "Manage user-defined track data files" to go to "User-defined tracks management" webpage.
User-defined tracks management webpage allows you to upload, delete and view Hi-C track files available in our HiView.
A Hi-C track file is a 9-column csv file (comma-delimited), with Columns 1-9 respectively as (1) Frag1.ID, (2) Frag1.Chr, (3) Frag1.StartBp, (4) Frag1.EndBp, (5) Frag2.ID, (6) Frag2.Chr, (7) Frag2.StartBp, (8) Frag2.EndBp and (9) Score. Some examples may be downloaded from the list of track csv files available.
In the "user-defined tracks management" webpage
- Upload data files - To upload a 9-column csv file, use "Upload Track" button.
- Delete data files - To delete a 9-column csv file, use "Delete Track" button.
- List of data files available to use - A list of 9-column csv files available is shown in the webpage and users can "Download" to view these csv files for some examples on how to prepare user-defined track files.
- Associate data files with user-defined tracks - To associate some specific csv files with User-defined Hi-C tracks 1-3, use "Associate with Track 1", "Associate with Track 2" and "Associate with Track 3" buttons.
The use and configuration of user-defined Hi-C tracks are the same as our usual Hi-C tracks. HiView will plot each Hi-C track as the "histogram" with the height defined by the "Score" column. If want to plot the height other scales (say logarithm 10 scale), please put the logarithm transformed scores in your prepared 9-column csv files. For example, users typically plot log10 (p_value) instead of raw p_value.
|
|
|
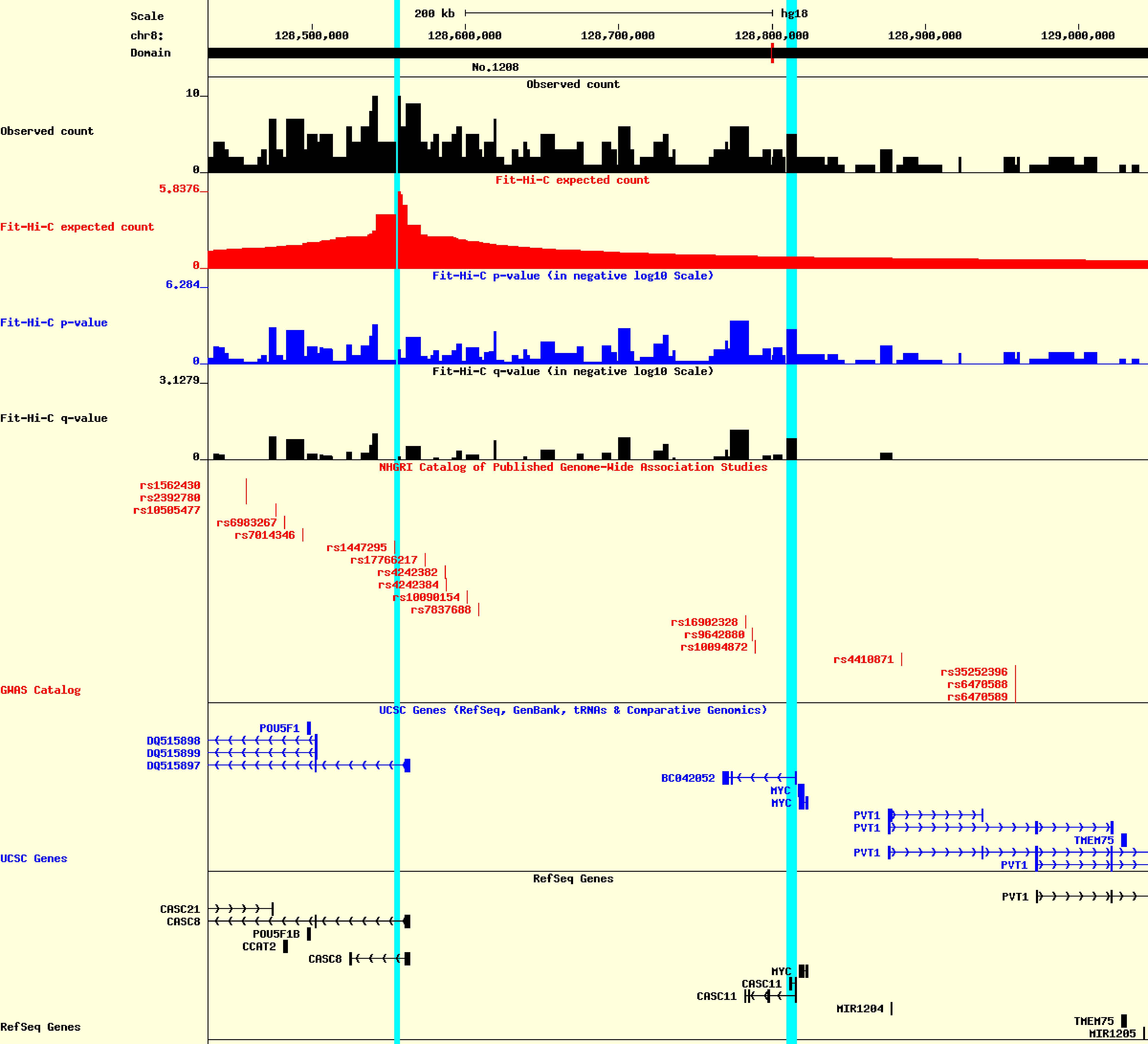
| An example Hi-C data anchored at SNP rs1600249 |
|
|
|
|---|
| |
An Hi-C data anchored at SNP rs1600249.
- Background
- SNP rs1447295 (identified in a GWAS study)
- HiView figure of SNP rs1447295 in the default setting
- Navigate and fine tune the viewing window
- Customize the display mode of tracks
- Customize the setting of the HiView figure
- Checking the gene function
- Detect the regulatory elements
The HiView figure generated following the above procedure will be similar to this.
|
|
|
| Other Hi-C Genome Browsers |
|
|
|
|
|